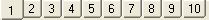Layers
The layers function is new to version 6. This powerful tool allows you to arrange the windows onto layers. A layer is essentially another copy of the Analysis software open with the data linked in with the data you currently have open. You can toggle between the different screens by using the navigation tabs at the bottom of the main window:
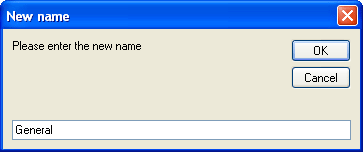
To select a tab, you left click on it. You can rename the tabs as you see fit, by right clicking on the tab, which will bring up a dialog asking you to enter a new name for the layer:
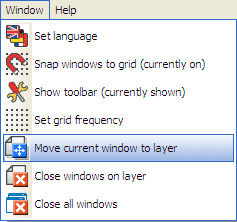
There are two ways of getting windows onto a layer. You can either select the layer you want the window on, and open the window on that layer, or you can move a window from the currently layer to another. You access the layer controls through the > Window menu:
Once you have a window open, if you wish to send it to a different layer, select the window, then go to > Window > Move Current Window To Layer, and then choose which layer you wish to send the window to.
If you have finished with the layer, you can close all the windows on the current layer by going to > Window > Close Windows On Layer. You must have the layer you wish to close the windows on selected when you click this option.
If you wish to close all windows on all layers, go to > Window > Close All Windows.
If you have created a layout you wish to use again, go to > File > Advanced Load/Saves > Save Screen Layout. More information on Loading and Saving can be found here.
As you start up the program, you will be prompted if you want to load the default layout from a file, which take a few seconds to open up a lot of predefined windows and settings, and organise them into the different layers, which have been renamed, detailing what the layer is used for. Once this process has passed, you will be able to quickly switch between the layers, allowing you to look specifically at the different measurements and to control different aspects of your data and how you analyse and compare it.